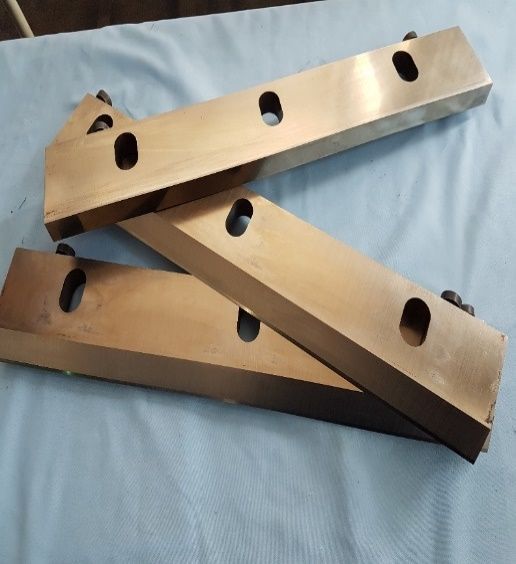
Enhancing Industrial Blades with Advanced Coatings

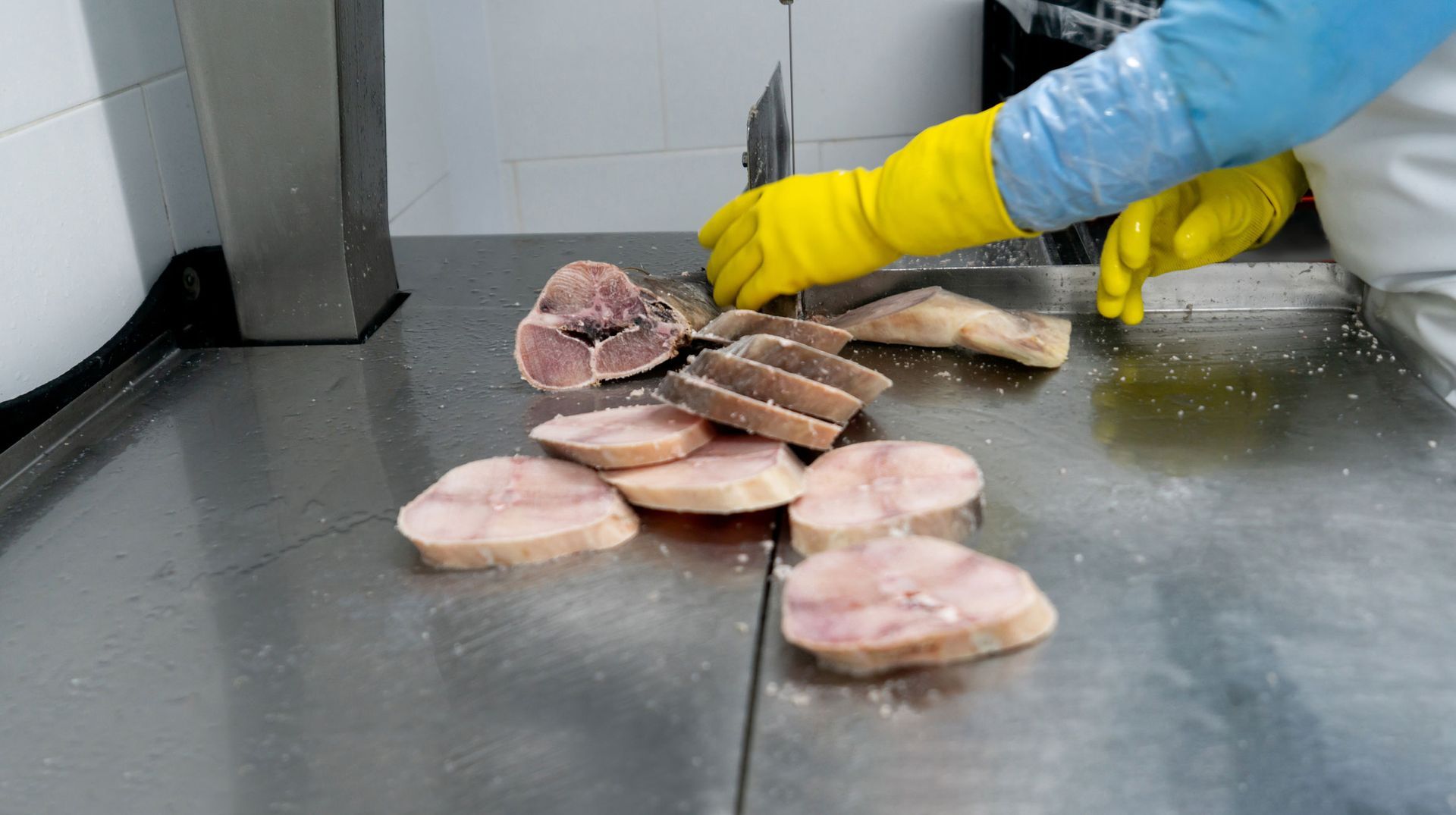
Industrial blade coatings play a pivotal role in elevating knife performance across paper, film, food processing, and metalworking lines. By applying specialized surface treatments, manufacturers unlock gains in wear resistance, friction reduction, and corrosion protection—translating into longer service intervals, cleaner cuts, and lower total cost of ownership.
Benefits of Blade Coatings
- Extended Wear Life: Hard ceramic or DLC (diamond-like carbon) layers can deliver 2–5× longer wear resistance compared to uncoated steel.
- Reduced Friction & Build-Up: Low-surface-energy coatings like PTFE or MoS₂ minimize material adhesion, preventing gumming and easing cleanup.
- Corrosion Protection: Stainless or alloy steels gain an added barrier against oxidative or chemical attack, critical in wet or corrosive environments.
- Consistent Cut Quality: Uniform coatings maintain edge geometry and eliminate micro-burrs, ensuring cleaner slices and fewer rejects.
Types of Industrial Coating Technologies
- Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Applies nanometer-thin TiN, TiCN, or DLC films under vacuum for superior hardness and adhesion.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Deposits carbide-based layers at elevated temperatures—ideal for high-temperature cutting blades.
- Thermal Spray Coatings: Sprayed-on ceramics or tungsten carbide for thick, rugged overlays on sacrificial wear parts.
- Liquid Polymer Coatings: PTFE-based dip or spray coatings that bond to steel, reducing friction and food-grade adhesion.
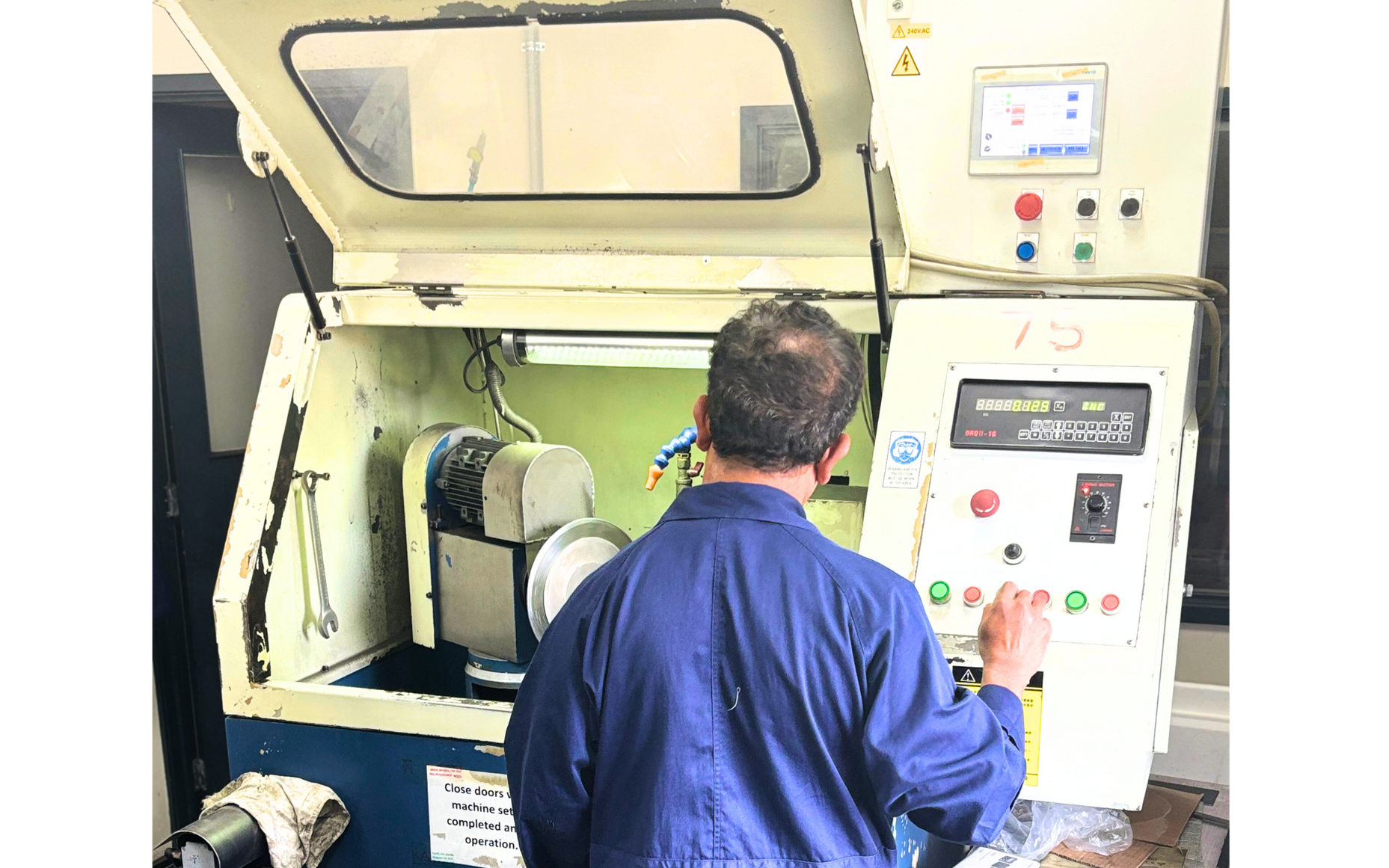
Coating Application Processes
- Surface Preparation: Precision grit blasting or chemical etch to remove oxides and create bonding sites.
- Deposition Control: CNC-guided fixtures ensure uniform thickness (2–10 µm for PVD; up to 200 µm for thermal spray).
- Post-Coating Validation: Tape-peel tests, microhardness measurements, and profilometry confirm adhesion, hardness, and thickness specs.
Selecting the Right Coating
- Application Environment: Wet, abrasive, or high-temperature conditions dictate ceramic vs. polymer-based choices.
- Cutting Material: Food-grade blades often need FDA-approved polymers, whereas metal-shearing knives benefit from DLC or TiCN.
- Budget & Lifecycle: Balance upfront coating cost against projected blade-life extension and maintenance savings.
Conclusion
Strategically implementing industrial blade coatings empowers manufacturers to push production rates, slash downtime, and uphold pristine cut quality. By understanding coating technologies and matching them to your operating demands, you’ll maximize blade ROI and maintain a competitive edge in any high-volume processing environment.